
Home monitoring requires night vision. When keeping an eye on your driveway, grass, or entry points, night vision is essential for security. Modern security cameras with night vision enable homeowners to capture crisp video in complete darkness. You can make wise purchases if you understand how these technologies work and what to look for. In order to keep your property safe at night, this article discusses several types of night vision, camera features, and ways to enhance night performance.
How Does Night Vision Work in Security Cameras?
Infrared Night Vision Explained
Infrared night vision employs infrared (IR) LEDs to illuminate dark areas. These LEDs emit light that the human eye cannot perceive, but the camera sensor can detect. When activated, IR lighting enables the camera to capture black-and-white photographs in full darkness. When light levels fall below a specific threshold, most security cameras automatically convert to infrared mode. The number and brightness of IR LEDs determine how far and well the camera can see at night. Infrared is the most popular and cost-effective night vision modality; therefore, it is frequently used in home and commercial security camera systems.
Low-Light and Starlight Technology
Low-light and starlight cameras use very sensitive sensors to capture ambient light, such as moonlight or streetlights, and generate full-color photographs at night. Unlike infrared systems, these cameras do not use IR LEDs and instead enhance ambient light. Starlight technology improves low-light performance with bigger sensors and wider apertures, resulting in more clarity and detail. These systems are appropriate for regions with existing lighting and a need for nighttime color fidelity. While starlight cameras are often more costly than IR-based versions, they provide outstanding surveillance performance in low-light conditions.
Thermal Imaging Basics
Thermal imaging cameras detect the heat radiated by humans, animals, and objects. Instead of using light, they use heat radiation to generate pictures. Warmer items seem brighter or distinct in comparison to cooler backdrops, making intruders simple to notice even in full darkness or thick fog. Thermal cameras are less influenced by optical impediments such as smoke or vegetation, making them useful in high-security places or hazardous outdoor conditions. While thermal imaging is often more costly, it provides consistent performance when standard cameras may fail. They are best utilized in conjunction with other technologies to provide a comprehensive surveillance solution.
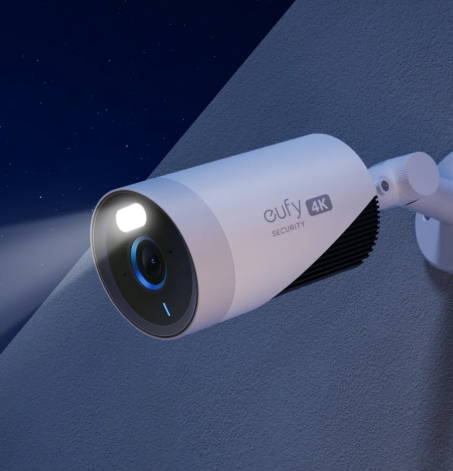

What to Look for in a Night Vision Security Camera?
IR Range and LED Count
The IR range is the distance a camera can see in the dark, which is commonly measured in feet or meters. A greater IR range enables the camera to take good photographs of distant objects at night. Equally critical are the quantity and strength of IR LEDs that give the appropriate light. More LEDs typically result in greater night vision capabilities, although positioning and lens design also influence output. For outdoor applications, use cameras with a minimum IR range of 65-100 feet. Make sure the LEDs are evenly positioned to eliminate hotspots and ensure consistent visibility throughout the field of vision.
Image Quality and Resolution
High-resolution night vision cameras produce crisper pictures, making it easier to see people, license plates, and other important information. Aim for at least 1080p Full HD quality; however, 2K or 4K cameras provide even more clarity, particularly when zooming into recorded footage. Image sensors, bitrate, and video compression are all factors that impact video quality. A good sensor combined with night vision capabilities may greatly improve visibility in low light. Crisp, well-lit photographs enhance detection and evidence collecting; therefore, resolution should be a key priority. When evaluating choices, consider image quality, storage requirements, and available bandwidth for maximum performance.
Smart Features and App Integration
Motion detection, customisable alarms, two-way audio, and remote access via mobile applications are among the capabilities available with smart security cameras. These capabilities enable customers to monitor their property in real time and respond promptly to issues. Integration with digital assistants such as Alexa or Google Home increases convenience by allowing voice commands and automation. Some applications provide improved night vision settings or allow you to adjust the IR light level. Look for solutions that include cloud storage, local backup alternatives, and encrypted data for further security. For complete monitoring, consider cameras that are part of broader Home Security Systems for enhanced functionality.
Tips to Improve Night Vision Performance
Proper Camera Placement
The correct camera location is extremely important for night vision clarity. Avoid pointing cameras straight at strong lights, such as streetlamps or windows, since this might generate glare and wash out photographs. Position them at angles that provide for an unobstructed view of the area. Mount cameras at a height that allows them to cover more land while remaining near enough to detect faces and objects. Avoid installation near reflective surfaces such as glass, since they can bounce IR light and degrade image quality. Adjust angles at night to assess real performance, ensuring that blind spots and low-light regions are reduced.
Keeping Lenses Clean
Dirty lenses can significantly diminish the efficacy of night vision. Dust, smudges, raindrops, and cobwebs may all scatter infrared light and obscure a picture. Regularly wipe the lens with a microfiber cloth and lens-safe cleaning solution. If you have outside cameras, examine them at least once a month or after a storm. Use weatherproof coverings or hoods to keep them out of the elements. Keeping the lens clean ensures that the film is crisp and well-lit, and it also avoids false motion alerts due to dirt or insects. A clean lens protects the integrity of the security feed, especially during critical low-light hours.
Reducing Ambient Light Reflection
Ambient light reflections can damage night vision, particularly when infrared LEDs bounce off surrounding surfaces. Common culprits include walls, window sills, and things too close to the camera. To reduce this, avoid pointing the camera toward reflective surfaces or glass. To block IR bounce-back when installing behind glass, use foam or rubber gaskets around the lens. Painting the surrounding reflecting surfaces in matte hues is also beneficial. Light interference is reduced by keeping the camera at a proper distance from surrounding objects. Reducing these reflections ensures that your night vision equipment runs smoothly and delivers clear, accurate footage every time.
Conclusion
Choosing the best night vision camera requires learning how different technologies function and assessing essential features that are important to you. Every sort of sensor, from infrared and starlight to thermal imaging, has its own set of advantages. To obtain the greatest value, consider the IR range, resolution, and smart features. Also, basic maintenance and appropriate installation may dramatically improve performance. With the proper configuration, night vision may be a formidable tool for securing your house day and night. Use this guide to make educated judgments and take the next step in creating a more intelligent, safer security system.